- Home
-
- The entrepreneurial Journey: Navigating the Path to Success
-
- Make a Strategic Decision for Your Business
Make a Strategic Decision for Your Business

What is your business based on?
Launching a new business is a multifaceted endeavor that demands careful consideration of various aspects.
To navigate the complexities of the business landscape, it’s crucial to integrate the insights gained from thorough analysis conducted during preliminary lessons.
A business, like a finely tuned machine, operates within two overarching macro-systems: the external world and the internal company ecosystem.
The principles outlined in the Business Model Canvas (BMC) provide a structured framework to grasp these intricacies and formulate a solid foundation for your business idea.
In the upcoming session, we will introduce various patterns outlined in the Business Model Canvas (BMC), accompanied by their advantages and disadvantages.
Our ultimate goal is to provide you with a comprehensive perspective and, furthermore, a strong foundation to begin outlining your business concept using the BMC application.
Consider broadening the scope of your BMC, leveraging these proven patterns. These strategies have been embraced by major global corporations, and we have strong confidence that their application to your idea will substantially enhance its prospects for success.
Entrepreneur's Toolkit: Turn Your Idea into a Successful Product
Prior to commencing the initial lesson of this course, it is of paramount importance that, as entrepreneurs, we initiate the process by downloading your toolkit.
For this course, the fundamental versions of the compelling apps are available at no cost.
These applications are exceptionally beneficial, as they will be employed to concentrate on developing your business idea throughout the entire duration of the course.
The Subscription Business Model: Sustaining Success
The Subscription Business Model is a formidable instrument for a company’s growth strategy. Its power lies in the ability to generate recurring and predictable revenue, benefitting both the company and its subscribers by ensuring business stability and user convenience.
This model encompasses a broad spectrum of value propositions, ranging from physical and digital products to an array of services.
Understanding the versatility of this business model can spell the difference between the success of a new venture or the revival of an existing one.
🤝 The Subscription Business Relationship
At the heart of the Subscription Business Model is the customer relationship. The longer this relationship endures, the more valuable the customer becomes to the business.
💡 How Subscription Business Model Revenue Flows
The primary challenge for companies embracing the subscription model is user retention. Unlike businesses reliant on one-time sales, subscription-based companies rely on maintaining their customer base for revenue generation. Consequently, delivering high-quality products and services becomes paramount to prevent customer churn—customers leaving for competitors.
Customer acquisition for subscription companies follows the same principles as any other business: marketing. However, there’s a crucial difference in marketing planning. To prevent subscription fees from becoming a burden, these companies often offer affordable pricing. As a result, it takes these companies longer to recoup their customer acquisition costs (CAC).
In essence, subscription companies must meticulously manage their acquisition costs to ensure long-term sustainability. A commonly employed strategy is the freemium model, enticing top-of-the-funnel users with a free offering and then converting a portion of them to a premium paid version. Once a company builds its subscriber base, it must consistently deliver a value proposition that aligns with user expectations. Failure to do so will lead to subscription cancellations. Thus, subscription-based businesses must thoroughly understand their target audience and their needs.
In contrast to traditional businesses, subscription companies invest more time, energy, and capital in subscriber retention while striving to reduce acquisition costs. When executed successfully, this approach cultivates satisfied users who not only remain loyal but also become brand advocates.
🌟 Popular Subscription-Based Businesses
The Subscription Business Model proves effective across a wide spectrum of industries, including:
Streaming Services: Companies like Netflix and Spotify leverage this model to offer vast content libraries. Customers access content as long as they maintain their subscriptions. Some, like Spotify, also employ the freemium strategy.
Monthly Subscription Boxes and Kits: These businesses have seen exponential growth. They offer curated boxes or kits for various needs, from food and wine to baby clothes, delivering convenience to subscribers.
Software: Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies opt for this model over one-time purchases. SaaS ensures recurring revenue while continually enhancing the product.
Recurring and Long-Standing Services: Industries like rentals, leasing, and insurance rely on subscriptions. Customers pay regularly for ongoing access to these services.
💰 Key aspects ot keep in mind
The Subscription Business Model offers stability and significant sales potential. However, it requires careful consideration of marketing strategy and planning.
Success hinges on goal-setting, tracking key indicators, delivering quality, and nurturing customer relationships.

Real-Life Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Considerations for Financial Impact:
Cost Efficiency: Unbundling necessitates a granular approach to Key Activities, enabling efficient resource allocation and cost management.
Scalability: Specialized components can be scaled independently, optimizing costs and resource utilization as demand fluctuates.
Revenue Streams: By monetizing internal assets, such as technology or expertise, additional revenue streams can be unlocked.
Resource Allocation: Allocating resources to specialized Key Activities maximizes value delivery and minimizes waste.
Competitive Edge: Unbundling allows businesses to excel in specific areas, enhancing their competitive edge and market positioning.
The Long Tail Business Model: Revolutionizing Sales and Markets
This model revolves around diversity, aiming to sell an array of niche products, each with modest individual sales but collectively contributing to substantial overall revenue.
Thanks to search engines and precisely targeted online media, this business model has thrived, allowing niche businesses to efficiently connect with their audiences like never before.
🚀 Unlocking the Long Tail
Historically, businesses concentrated their efforts on marketing and selling a few highly profitable mainstream products.
While these products generated substantial sales, they often incurred significant initial costs. In contrast, the Long Tail Business Model centers on selling numerous unique items that cater to niche markets.
This model doesn’t rely on superstar bestsellers; instead, it emphasizes offering a variety of hard-to-find products to diverse niche consumers.
The name “Long Tail” derives from the graph that illustrates this concept, depicting a shift away from traditional sales concentration at the curve’s beginning to a demand for a wide range of products along the curve.
💡 Advantages of the Long Tail
The Long Tail Business Model boasts several key advantages:
Cost Efficiency: At its core, this model reduces costs associated with stocking, distribution, and logistics. For online products, the benefits are even more significant, with minimal storage expenses and near-zero distribution and logistical costs. The internet facilitates direct connections between buyers and sellers, reducing the need for physical retail space.
Crowdsourced Diversity: Think of Google as a vast community of individuals and businesses contributing to an enormous database, creating and interlinking content across the web. This collaborative effort enables consumers to discover a wide array of products and information.
Data-Driven Insights: Leveraging deep customer intelligence, engines gather data to enhance recommendations and product development. Recommendation engines can suggest niche products aligned with individual customer preferences, tailoring offerings to specific tastes. This data-driven approach extends to content creation, with platforms like Netflix using insights to produce content targeted at distinct niche audiences.
🌍 Impact of the Long Tail
The Long Tail Business Model has ushered in a significant shift in the economy. Traditionally, blockbuster products accounted for about 80% of sales, but this figure has dropped to less than 50%, highlighting the rise of long tail products. In this economy, inventory, logistics, and warehousing costs are substantially reduced, and competition is less concentrated due to the dispersed nature of the market. Online products, in particular, thrive in this environment.
To succeed in this business model, companies and entrepreneurs must ask themselves a fundamental question: Does my business leverage the vast and widespread distribution channels available? 🤔
Real-Life Example: Spotify
Considerations for Financial Impact:
Content Acquisition: Costs associated with securing a diverse range of content impact profitability.
Personalization Algorithms: Investment in algorithms that curate personalized content enhances user experience and retention.
User Retention: Niche content and personalization foster user loyalty, driving recurring revenue through subscriptions.
Platform Scale: As the platform scales, content acquisition costs may decrease, enhancing the platform’s financial viability.
Revenue Growth: Diverse content increases engagement, leading to more subscriptions and revenue growth.
The Thrifty Path to Success: The Low-Cost Business Model
The Low-Cost Business Model is a savvy strategy in which a company offers products or services at competitive prices to stimulate demand and capture a significant market share.
While it can be adopted by various companies, it’s particularly advantageous in scenarios where there’s no distinct competitive edge, or when achieving economies of scale through production volumes makes this cost-efficient approach a wise choice.
🤔 Understanding Cost Advantage
In essence, a business embraces the cost advantage when it can produce goods or provide services at a lower cost than its rivals. This advantage can be leveraged in two primary ways:
Price Leadership: By setting prices below competitors, attracting more customers, and gaining market share. Although this may entail thinner profit margins, the sheer volume of sales compensates for it.
Profit Maximization: By pricing products on par with competitors while maintaining a cost structure that’s lower. This approach results in increased profit margins.
To create a lean cost structure, these companies often benefit from:
✅ Low-Cost Raw Materials
✅ Efficient Processes, Technologies, and Operations
✅ Streamlined Distribution
✅ Cost-Effective Sales Strategies
✅ Outsourced Services
✅ Lean Manufacturing Tactics
Regardless of customer demographics, people always compare prices and appreciate affordability. Consequently, attracting customers through competitive pricing is a valuable strategy. However, it comes with its own set of challenges and advantages.
🌟 Advantages of the Low-Cost Business Model
Bigger Profit: A lean cost structure can yield higher profit margins, offering customers the same value as competitors but at a lower price.
Improved Market Share: Customers often opt for similar value propositions at lower costs. Over time, this choice results in more business, expanding market share.
Sustainable Business: A lean cost structure reduces risks, making the business more resilient during crises and uncertainties.
Reinvested Capital: Increased margins build a capital reserve, which can be reinvested to fuel growth or expansion.
Reduced Competition: Offering low-cost products or services forces competitors to reduce prices. Established businesses may find it challenging to adapt, giving newcomers an edge.
Increased Sales: Cost leadership often attracts a higher volume of customers, especially in the early stages, aiding in covering initial investments.
Close Relationships: Cost reduction strategies, like maintaining close communication with customers and suppliers, create trust and help optimize costs.
🚫 Disadvantages of the Low-Cost Business Model
Price War: Competitors may respond with price cuts, potentially leading to a profit-diminishing battle for the lowest prices.
Poor Supplier Relationships: Pushing suppliers to their limits in terms of pricing and deliveries may strain relationships or result in subpar materials.
Low-Profit Margins: Fierce competition or supplier negotiations gone awry can lead to meager profit margins and limited reinvestment capabilities.
Poor Quality Perception: Offering lower prices can sometimes be misconstrued as compromising quality, making it challenging to introduce higher-priced, quality products.
Harmful Financial Cuts: To maintain a lean cost structure, cost-cutting measures may inadvertently harm operations or diminish the value proposition.
Reduced Innovation: R&D investments may be perceived as expensive, limiting the introduction of innovative products or services to the market.
High Sales Volume Requirement: Cost leadership hinges on high sales volumes for profitability, often necessitating the resources and reach of large brands.
The benefits and challenges underscore that the low-cost business model can create a unique competitive advantage. However, its suitability varies across businesses, as it may limit adaptability to changing circumstances.”
This rephrased content maintains the core ideas from the original text while offering a more concise and engaging presentation.

The Multisided Platform Business Model: Where Connections Count
The Multisided Platform Business Model has been embraced by some of the globe’s most valuable startups, including the likes of PayPal, Uber, Alibaba, eBay, and Facebook.
However, contrary to popular belief, this model isn’t a recent phenomenon;
it has roots dating back centuries. Nevertheless, the advent of the internet and the digital realm has propelled Multisided Platforms (MSPs) to prominence.
This versatile business model is applicable to startups, emerging enterprises, and established brands alike.
The success stories of companies adopting this model have made it an enticing choice for many aspiring entrepreneurs.
So, what does it take to develop a Multisided Platform akin to Uber or YouTube? Let’s delve into the intricacies of this business model.
🧐 Demystifying the Multisided Platform Business Model
At its core, the Multisided Platform Business Model serves as a conduit, connecting two or more participant groups while assuming an intermediary role. Its value proposition revolves around facilitating this connection, making it easier for these groups to discover and interact with each other.
🔗 Connecting the Dots
Most often, these companies unite two groups. For instance, businesses like eBay, Uber, Airbnb, and PayPal primarily cater to two sides: buyers and sellers, drivers and passengers, hosts and guests, merchants and consumers. These are frequently referred to as “two-sided platforms” because they consist of a supply side and a demand side.
Yet, some companies foster interactions among multiple groups, exemplified by Facebook. Facebook brings together users, advertisers, content developers, and more. In this scenario, the most substantial group—the users—typically serve as consumers, availing of the platform’s services without direct payment. On the other side, there are customers, a smaller group responsible for generating revenue. Take Facebook’s advertisers, for instance—they pay to reach their target audience, who also happen to be users of the platform.
🎯 Value Proposition of Multisided Platforms
In simple terms, the value proposition of Multisided Platforms revolves around matchmaking. These platforms neither produce content nor deliver services themselves; instead, they serve as intermediaries. To effectively fulfill this intermediary role, platforms must be compelling. For instance, if Uber had developed its app but failed to garner interest or usefulness among users, it wouldn’t attract passengers or drivers. As a result, there wouldn’t be demand for drivers. Similarly, if YouTube couldn’t monetize its platform, it would merely serve as an entertaining video repository. Multisided Platforms create value for participants by:
Facilitating Exchange: By connecting buyers and sellers or service providers with consumers, these platforms streamline transactions. New businesses and sellers can enter the market with minimal investment, saving particularly on advertising. Buyers, in turn, enjoy the convenience of purchasing goods from the comfort of their homes, often at more affordable prices.
Providing a Digital Hub: Social media and content platforms offer a digital ecosystem where users become content generators. Users feed the platform with content and valuable data for the demand side. Consequently, highly targeted marketing campaigns become feasible.
🔄 Multisided Platforms and Network Effects
In the realm of Multisided Platforms, network effects play a pivotal role and can be either positive or negative, amplifying or diminishing the business’s value. To be valuable for all participant groups and, subsequently, a profitable enterprise, Multisided Platforms must attract users—more users translate to higher value. There are two types of network effects:
Direct Network Effects (Same-Side): Here, participants on one side of the network influence each other. A prime example is social media, like Facebook or Instagram, where increased users enhance the platform’s appeal.
Indirect Network Effects (Cross-Side): This is the more common form, where participants on one side affect those on the other. For instance, drivers and passengers or product variety influence buyers.
💰 Revenue Generation for Multisided Platforms
One of the most prevalent revenue streams for MSPs involves transaction fees. These fees may be fixed or a percentage of the transaction value, often transparent to customers, as seen in many e-commerce platforms. In other cases, platforms charge for access, as exemplified by dating sites. Lastly, enhanced access, like premium search results on Google, constitutes another revenue source.
🚀 Challenges Faced by Multisided Platforms
While we’ve highlighted successful MSP examples, it’s crucial to acknowledge that many attempts in this domain don’t reach the summit. The Multisided Platform business model presents several challenges en route to success. Chief among these is the need for consumption: no transactions, no revenue. Consequently, companies must consistently acquire and retain audiences. Establishing an initial user base can be arduous, and engaging them necessitates delivering a high-quality service. The Multisided Platform business model is conceptually straightforward, yet it thrives only when all participants remain actively engaged, ensuring the business’s enduring vitality.”
Real-Life Example: Airbnb
Considerations for Financial Impact:
User Acquisition: Expenses associated with attracting and retaining users across multiple segments affect profitability.
Value-Added Services: Offering value-added services to both sides of the platform can drive additional revenue.
Network Effects: A growing user base amplifies the platform’s value, attracting more users and enhancing revenue streams.
Platform Moderation: Costs tied to ensuring trust, safety, and quality standards are maintained across the platform.
Transaction Fees: Revenue generation through transaction fees requires careful balancing to encourage transactions while remaining competitive.
Unlocking the Potential of Productized Services
Productized Services have ushered in a new era within the service industry, fostering innovation and addressing long-standing challenges. In this exploration, we delve into the workings of the Productized Services business model, its merits, its limitations, and the promising prospects it offers.
📜 A Brief Chronicle of Productized Services
The service industry has witnessed remarkable expansion over recent decades, leading to a surge in innovations across various sectors.
Productized services stand as one such innovation, playing a pivotal role in the industry’s rapid evolution.
These services are essentially packages of offerings with clearly defined parameters, terms, and prices.
As a result, customers who engage with these services are well-informed about what to expect in advance. While pinpointing the exact birth of this model is challenging, it has gained traction among freelancers and large service agencies alike.
🚀 Why Productized Services Ascended
Amid the service sector’s meteoric rise, its flexibility, a prized asset, paradoxically posed challenges. The malleability of services, while facilitating scalability and versatility, led to issues such as clients struggling to accurately estimate costs and anticipated outcomes.
Productized services emerged as a remedy to this quandary, offering consumers the vital elements of transparency and predictability.
Moreover, they provided businesses with a more dependable model concerning costs and revenue.
Examples of such services include WordPress (with its WP Speed Fix service), KENJI ROI (a specialist in Amazon listing optimization), and 50 Pound Social (a platform for social media content creation).
💰 Revenue Generation in Productized Services
Much like standard products within the service industry, productized services generate revenue by offering “intangible goods.” These encompass actions, access to specific resources, or other forms of benefits. What sets these services apart is their pre-packaged nature, complete with well-defined prices and parameters.
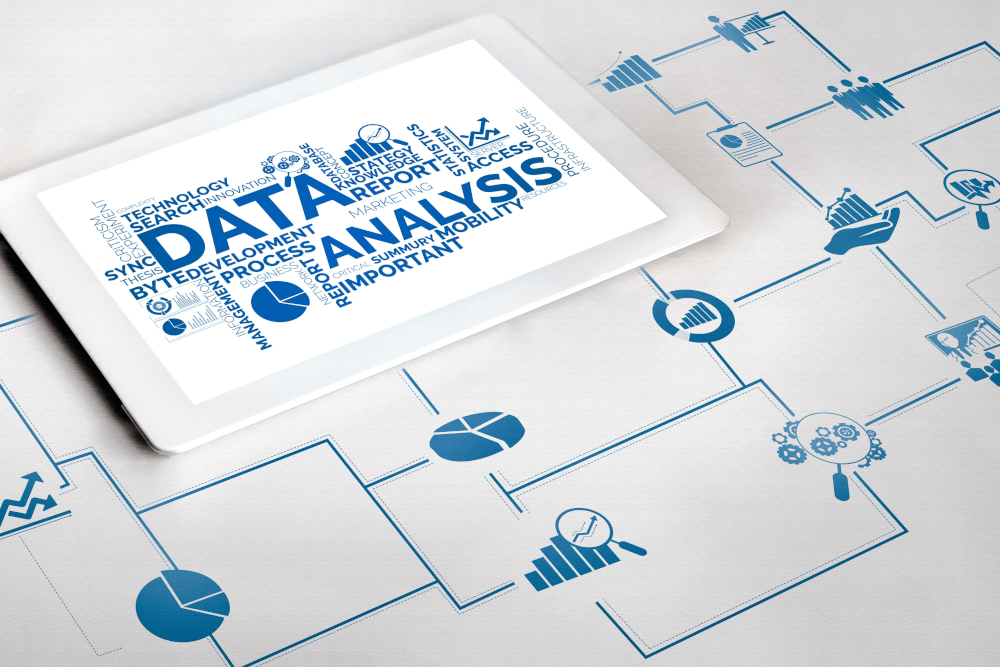
🎨 The Productized Services Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a closer look at the Productized Services business model canvas:
🔍 Customer Segments: Individuals seeking services but preferring standardized packages with fixed terms and prices.
🎁 Value Proposition: The advantages of Productized Services over other service forms include enhanced standardization, reduced risks associated with non-standardized services, lower supervision requirements, and a more dependable income source.
🛒 Channels: Productized services can operate via various channels, with social media, mobile apps, internet services, and e-commerce platforms gaining popularity.
💬 Customer Relationships: These companies can engage with customers through diverse relationship types.
💸 Revenue Streams: Revenue primarily comes from selling standardized services to interested buyers.
🔑 Key Resources: An innovative business strategy, emphasizing service productization.
🏭 Key Activities: Offering a wide range of services and standardizing them into various packages.
🤝 Key Partners: Collaboration with other businesses essential for delivering the core value proposition.
💲 Cost Structure: Costs encompass fixed expenses (e.g., rent, machinery, salaries) and variable costs (e.g., delivery, payment processing, wages).
🥊 Competitors: Productized services face competition from companies offering greater customer freedom and flexibility.
🔍 SWOT Analysis: Evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the Productized Services model:
Strengths:
Predictable revenue and cost structure.
Enhanced auditability and efficiency.
Incentives for price inflation reduced.
Easier employee training due to standardization.
Generally considered more credible and scalable.
Weaknesses:
Less flexibility compared to non-standardized services.
May limit the target market.
Offers less personalization.
Initial standardization efforts may require substantial time and monetary investments.
Opportunities: Focus on harnessing the benefits of Productized Services while addressing their limitations, particularly in terms of flexibility and personalization.
Threats: Non-standardized services continue to offer greater personalization and flexibility.
Real-Life Example: Google
Considerations for Financial Impact:
Cost of Freemium: Offering free core services involves covering costs while enticing users to explore premium options.
Ad Monetization: Monetizing through ads requires balancing user experience with revenue generation.
Conversion Rate: Converting free users to paid users determines the success of the freemium model.
Premium Offerings: Premium offerings should offer substantial value to justify the cost and encourage upgrades.
Sustainable Revenue: Maintaining a balance between free offerings and premium services is crucial for long-term revenue sustainability.
0€
Free contentThe entrepreneurial Journey
Throughout this course, you'll explore:
The effective use of BMC and SWOT to validate your business idea.
Revealing insights into your competitors and their hidden strategies.
Leveraging their weaknesses through appropriate business tactics.
Ultimately, identifying the optimal pricing strategy for your product.
300€
ONE2ONE - SINGLE LESSONDo you have a particular lesson in mind that you'd like to revisit, customized to your specific business situation?
Take advantage of our complimentary 20-minute phone consultation, during which you can share your BMC and SWOT analysis from the lessons.
We'll then arrange a personalized one-on-one session just for you.
1600€
ONE2ONE 7 LESSONSLooking to fortify your business case?
Share all the BMC and SWOT analyses you've developed during the course.
Seize the opportunity of our free 20-minute phone consultation, where you can discuss your primary objectives.
Following that, we'll organize seven one-on-one sessions to collaborate on refining your concept and taking it to the next level.